Ever wondered about that paper you sign at the doctor’s office? You know, the one that says “Medical Consent Form” at the top? Well, it turns out, it’s not just another piece of paperwork. It’s a pretty crucial link between you and your healthcare team.
What is a Medical Consent Form?
Think of it as your permission slip for the medical world. It’s the document that gives the green light for doctors to do their thing – whether it’s a treatment, a procedure, or anything in between. But here’s the kicker – it’s not just a signature; it’s a way of making sure you know exactly what you’re getting into.
In this blog post, we’re going to break down the ins and outs of Medical Consent Forms. We’ve got more than 17 templates in PDF and Docs formats coming your way. But it’s not just about the paperwork – we’re here to unravel why these forms matter, what goes into them, and how they help both you and your healthcare squad make informed decisions.
Ready to dive into the world of Medical Consent Forms? Let’s go!
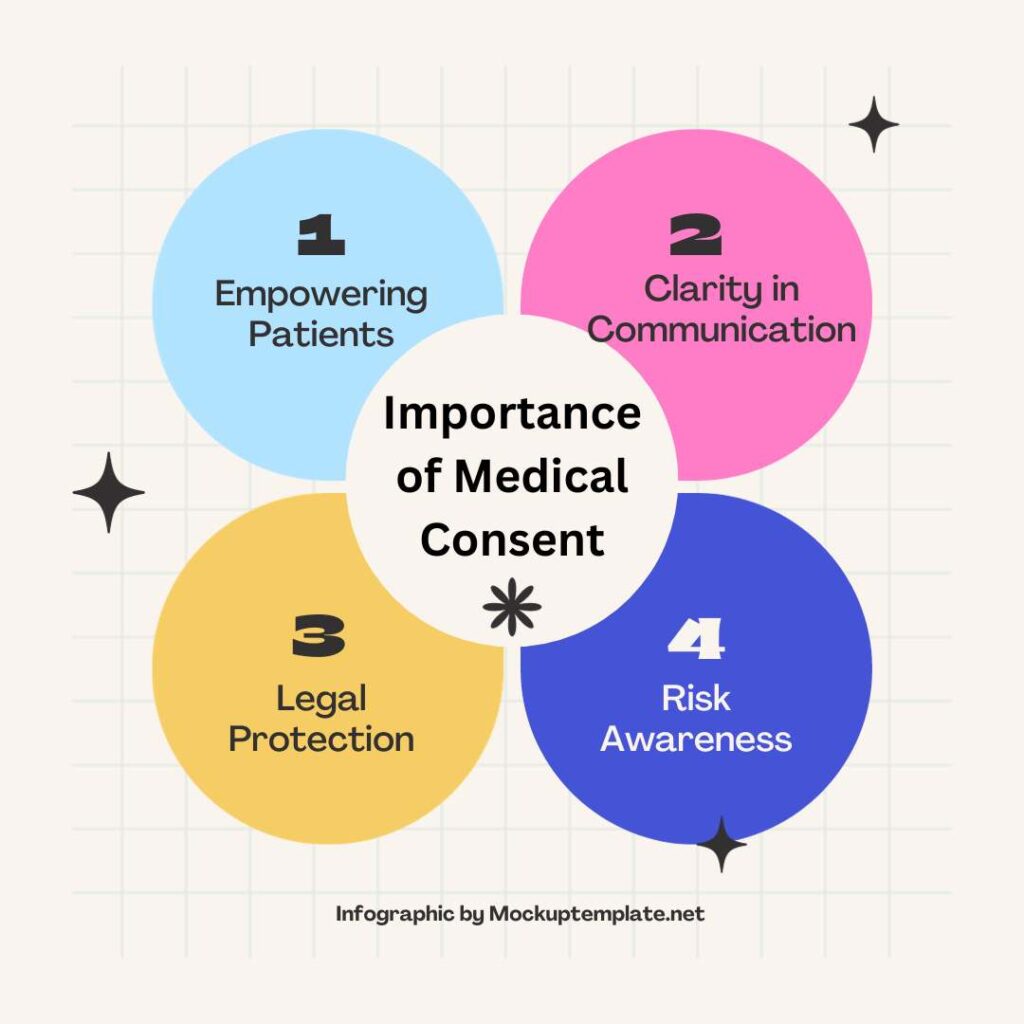
Importance of Medical Consent
When it comes to healthcare, understanding the significance of Medical Consent is paramount. It’s not just a bureaucratic formality but a cornerstone of patient autonomy and involvement in their own care. Here’s why it matters:
Empowering Patients:
Medical Consent puts the power in your hands. It ensures that you have a say in your treatment, allowing you to make informed decisions about your health.
Clarity in Communication:
Ever been handed a bunch of medical jargon and felt lost? Medical Consent is the remedy. It breaks down complex information into digestible bits, fostering clear communication between you and your healthcare provider.
Legal Protection:
From a legal standpoint, Medical Consent forms are a shield for both parties. They protect healthcare providers by confirming they’ve adhered to ethical standards, and they safeguard patients by ensuring their rights are respected.
Risk Awareness:
Life is full of uncertainties, and so is healthcare. Medical Consent doesn’t just list procedures; it outlines potential risks. This transparency prepares you for what might come, making the healthcare journey a less daunting one.
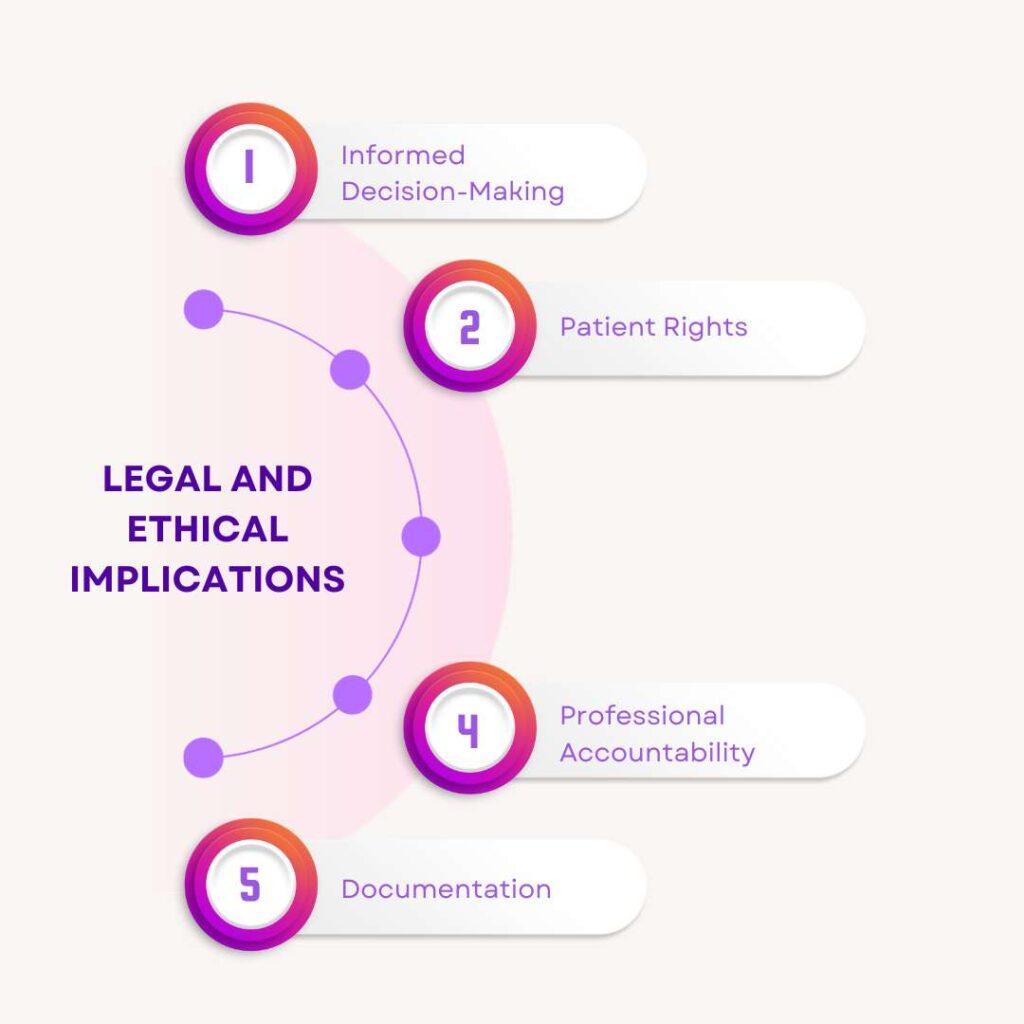
Legal and Ethical Implications
Behind every Medical Consent Form lies a web of legal and ethical considerations. It’s not just about signatures; it’s about ensuring that the medical journey is both lawful and ethical. Here’s a glimpse into the legal and ethical tapestry:
Informed Decision-Making:
Legally and ethically, the emphasis is on informed decision-making. Medical Consent ensures that you’re not just agreeing blindly but are aware of the what, why, and how of your treatment.
Patient Rights:
Your rights as a patient are paramount. Medical Consent is a tangible expression of these rights, acknowledging your autonomy in making decisions about your body and health.
Professional Accountability:
For healthcare providers, Medical Consent is a pledge. It’s a commitment to uphold professional standards and act in the best interest of the patient, both ethically and legally.
Documentation:
From a legal standpoint, proper documentation is crucial. Medical Consent Forms provide a trail of evidence that procedures were discussed, understood, and agreed upon, offering protection in case of disputes.
In essence, Medical Consent isn’t just paperwork; it’s a cornerstone of patient-centered care, intertwining legal protection and ethical responsibility.
What are the 4 types of medical consent?
There are generally four types of medical consent, each addressing specific situations and considerations:
Expressed Consent:
This is the most common form of consent, where individuals explicitly verbalize or provide written permission for a specific medical intervention. Expressed consent is obtained after the healthcare provider explains the details of the procedure, risks, benefits, and alternatives. It is essential for non-emergency situations.
Implied Consent:
Implied consent is inferred from a person’s actions or circumstances. It is typically applicable in emergency situations where obtaining explicit consent is not possible due to the urgency of the medical intervention. For example, if a person is unconscious and requires immediate medical attention, healthcare providers may proceed with necessary treatment under the assumption of implied consent.
Informed Consent:
Informed consent goes beyond a simple agreement. It involves providing the patient with comprehensive information about the proposed medical procedure, including its purpose, potential risks and benefits, and available alternatives. The individual is then empowered to make an informed decision based on a clear understanding of the situation. Informed consent is a vital aspect of ethical medical practice.
Minor’s Consent (Parental or Guardian Consent):
When it comes to minors (individuals under the age of 18), they may not have the legal capacity to provide consent independently. In such cases, parental or guardian consent is typically required. However, there are instances where minors, depending on their age and the nature of the medical treatment, may provide their own consent, particularly for confidential services like reproductive health.
Understanding these types of medical consent helps ensure that individuals’ rights are respected and that healthcare practices adhere to ethical and legal standards in various situations.

Who Can Give Consent?
Competent Adults:
Competent adults, those of legal age and sound mind, have the authority to provide consent for their own medical decisions. They hold the autonomy to make choices about their healthcare without the need for additional approvals.
Minors and Parental Consent:
In the case of minors, individuals below the legal age of adulthood, parental or guardian consent is typically required for medical procedures. This recognizes the limited legal capacity of minors to make independent healthcare decisions.
Consent for Individuals with Limited Capacity:
Certain individuals, due to mental illness, cognitive impairment, or other conditions, may have limited capacity to fully understand and make decisions about their medical care. In such cases, a legal guardian or appointed representative may provide consent on their behalf, following established legal procedures.
Emergency Situations:
In urgent and emergency situations where immediate medical intervention is necessary to preserve life or prevent serious harm, consent may be implied. Healthcare providers are authorized to proceed with necessary treatment without explicit consent, prioritizing the well-being of the individual.
Understanding who can give consent is crucial in ensuring ethical and legal healthcare practices, respecting the autonomy of individuals, and providing appropriate care in diverse situations.
Sample Consent Forms
Medical Consent Form

Printable Grandparent Medical Consent Form

Consent Form in Medical Billing

Emergency Medical Consent Form

Child Medical Consent Form California

Sample Medical Consent Form for Minor

Permission Medical Consent Form for Adults

Consent Form for Medical Treatment

Travel and Medical Consent Form for Minor

Employee Medical Consent Form

Notarized Medical Consent Form for Minor

School Trip Medical Consent Form

Release of Medical Information Consent Form

Parental Medical Consent Form

Medical Consent Form for Surgery

Patient Medical Consent Form

Common Mistakes to Avoid:
Inadequate Information:
One of the most prevalent pitfalls in the realm of medical consent is providing insufficient information. Informed consent hinges on a comprehensive understanding of medical procedures, risks, and alternatives. Failing to furnish patients with clear and detailed information can lead to misunderstandings and compromise the validity of the consent process.
Lack of Clarity:
Clarity is the linchpin of effective communication in healthcare. Ambiguous language, technical jargon, or convoluted explanations can cloud the comprehension of patients. Lack of clarity in the consent process jeopardizes the essence of informed decision-making, potentially resulting in misguided consent and complications down the line.
Failure to Document:
Proper documentation is not just a bureaucratic formality; it’s a safeguard for both healthcare providers and patients. Neglecting to meticulously record the consent process, including discussions, disclosures, and signed forms, leaves a void that can be detrimental in case of disputes. Documentation serves as a crucial reference point, validating the legality and ethicality of the consent obtained.
Steering clear of these common mistakes ensures that the process of obtaining medical consent is not just a procedural checkbox but a robust and transparent interaction, fostering trust between healthcare providers and patients.

Recent Changes and Developments:
Legal Updates:
Keeping pace with the dynamic landscape of healthcare, legal frameworks surrounding medical consent undergo continuous evolution. Staying informed about recent legal updates is paramount for healthcare providers and patients alike. Changes in regulations may impact the consent process, altering requirements or introducing new considerations. Regular updates ensure that practices align with the latest legal standards, reinforcing the integrity of the healthcare system.
Trends in Informed Consent Practices:
Informed consent practices are not static; they reflect evolving societal norms, technological advancements, and a deeper understanding of patient needs. Recent trends in informed consent include the integration of digital platforms for information dissemination, the emphasis on patient education through multimedia resources, and a heightened focus on shared decision-making. Exploring and adapting to these trends contributes to a more patient-centric and collaborative approach to healthcare decision-making.
Remaining attuned to legal updates and emerging trends in informed consent practices positions both healthcare providers and patients to navigate the complexities of modern healthcare with awareness and adaptability.
Conclusion:
Recap of Key Points:
In conclusion, medical consent is more than a signature—it’s a cornerstone of patient empowerment, legal integrity, and ethical healthcare. From upholding autonomy to adapting to change, understanding the diverse types of consent and avoiding common pitfalls ensures a collaborative journey toward informed and respectful healthcare decisions. Informed consent isn’t just a formality; it’s a commitment to transparency, communication, and patient-centered care.

